Download PDF (3.1 mb, PDF)
Download Patient Journey PDF (2.8 mb, PDF)
What is Hepatitis C?
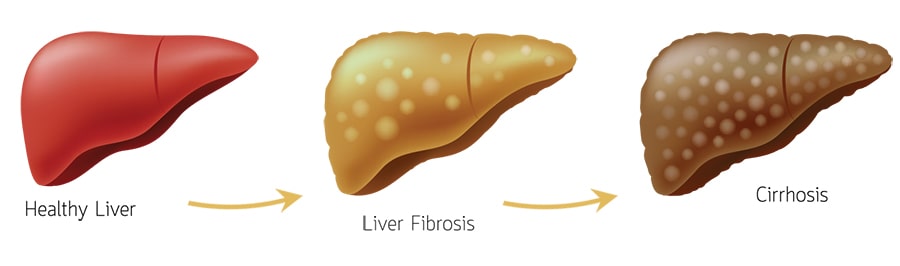
Hepatitis C is an infectious disease caused by a virus that attacks your liver. It damages your liver, leading to liver hardening (liver cirrhosis) which causes liver cancer and liver failure.
How does it spread?

Hepatitis C is primarily spread through exposure to infected blood, such as through raw wounds, piercings, tattoos or when needles or syringes are shared.
What to expect if Hepatitis C virus enters the body?
When a person is exposed to the Hepatitis C virus, the body will try to eliminate it to prevent it from staying in the body.
This is called an
ACUTE infection. Most people with acute infections have no symptoms, but some may experience yellow discolouration of the skin and eyes called “jaundice”.
What to expect if the Hepatitis C virus enters the body?
When a HCV infection is
chronic, it means the virus is going to stay in your body for longer.
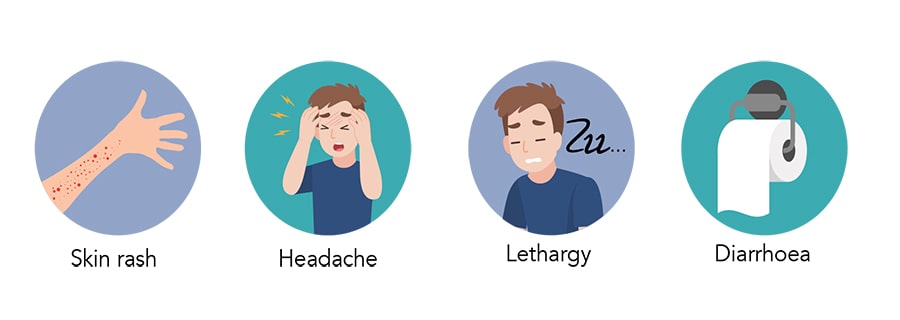
Such a person may be feeling the following symptoms:
- Tired quickly
- Poor appetite
- Low-grade fever
- Abdominal discomfort
- Skin rash
- Diarrhoea
What happens if the Hepatitis C virus stays in our liver?
The liver is a vital organ which helps to excrete toxins from our body. It also produces essential proteins, which ensure that you do not bleed easily and maintain your health.
A damaged liver is a ‘time bomb’ in our body as we are vulnerable to liver failure and cancer.
Liver cirrhosis - What is the fear?
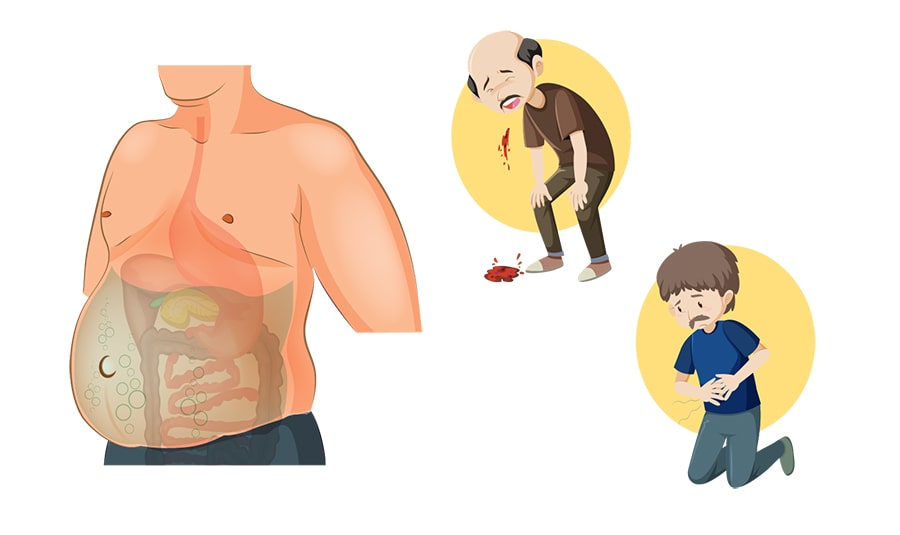
When a person has liver cirrhosis and liver failure, many things can happen.
- Extreme tiredness and not being able to concentrate
- Swelling of the abdomen and legs due to water accumulation
- Bleeding tendency
- Vomiting blood from bleeding vessels in your food pipe (oesophagus)
- Developing a deadly liver cancer
Advanced liver cirrhosis – The impact on your life
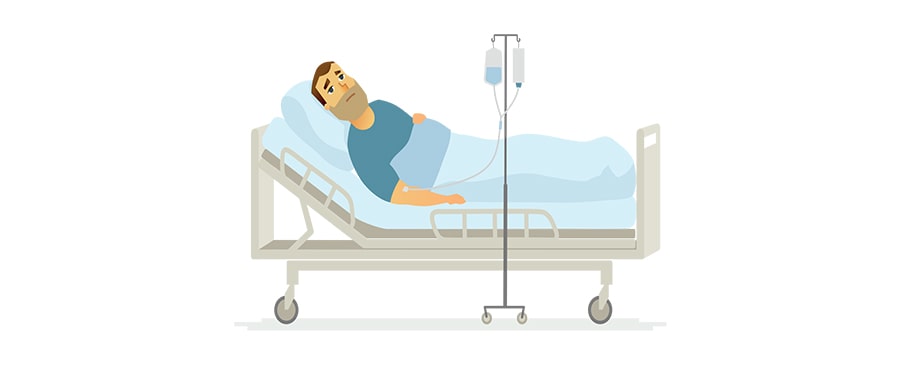
- You may not be able to work again
- You may not enjoy a normal lifestyle
- You will need to come to the hospital for clinic visits or hospitalisation frequently
- You may lose your ability in making decisions
- You may have shortened life expectancy
Why let all these things happen to you when you can prevent them?

Step Ahead!
- Test, get yourself
- Educated on Hepatitis C and,
- Treat it if you are tested positive.
How to test for Hepatitis C?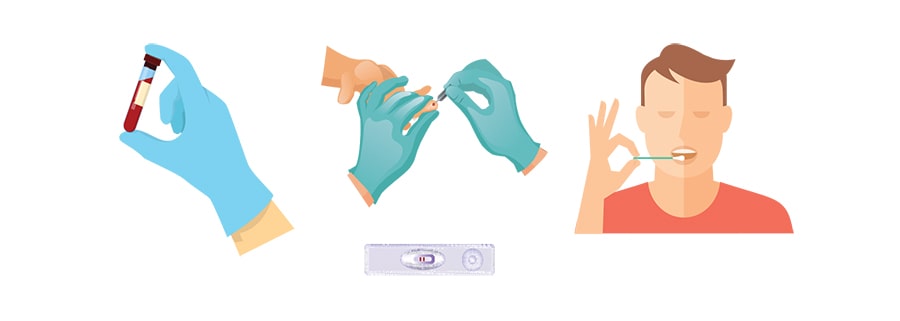
Hepatitis C can be readily detected using a blood test performed at a clinic or hospital.
The test is called Anti-HCV, which indicates previous
exposure to the virus.
This
does not confirm that you have an active infection.
Is there an easier way?
To make detecting Hepatitis C easier, we are currently confirming the effectiveness of a point-of-care test (POCT) using finger prick blood test and saliva. Your contribution to making this happen is very important!
How to confirm an active Hepatitis C infection?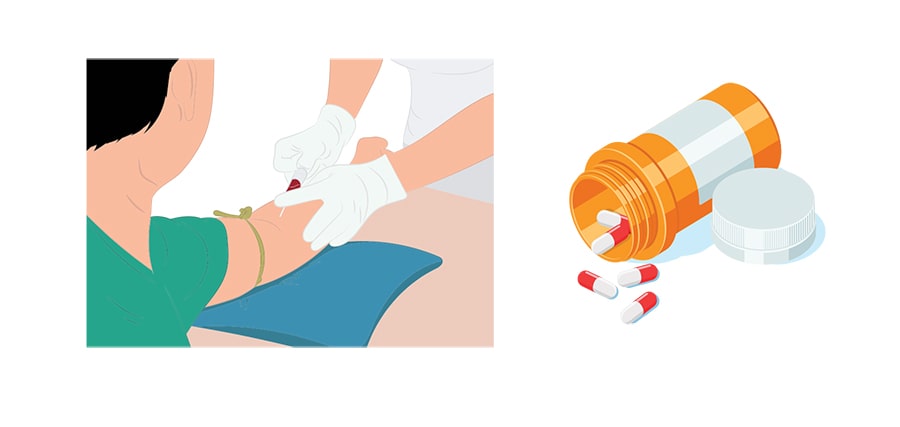
This test looks at the genetic material in your body used to reproduce the Hepatitis C virus.
Can it be treated?
- Yes!
- There are oral medications available that can treat Hepatitis C for almost everyone within 8 to 12 weeks
- No injection is required
- It is safe and tolerable
What if the Hepatitis C treatment was not successful this round?
Do not give up, as your doctor may discuss with you other treatment options using a different way. You still stand a pretty good chance of recovery if you can complete this treatment.
Have a question?
The following contact numbers may be helpful to you.
- Clinic 4B hotline - Tel: 6889 4445
- TTSH Level 4 Pharmacy - Tel: 6889 4353
- TTSH Level B2 Pharmacy - Tel: 6357 2040
- TTSH General Enquiries Contact - Tel: 6256 6011 Email:
[email protected]