Download English PDF, 1MB, PDFDownload Chinese PDF, 784KB, PDF
What is Gout?
Gout is a common form of arthritis that causes sudden severe episodes of pain, swelling, redness and warmth of joints. These symptoms are caused by the formation of small uric acid crystals in and around the joints.
What is Uric Acid?
Uric acid is a normal waste product from the breakdown of purines (chemical compounds in your DNA and RNA) found in most food and is removed from the body by the kidneys.
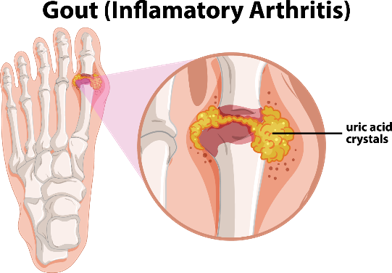
Deposition of uric acid crystals in the big toe resulting in a gout attack.
Who are at Risk of Gout?
Gout is the most common inflammatory arthritis in men over the age of 40. Women are usually protected from gout until after menopause.
Gout may occur independently, or as a complication of other conditions such as kidney failure and leukaemia. It is also associated with:
- Diabetes mellitus
- High blood pressure
- High cholesterol
- Some medications that may aggravate or trigger gout
Although hyperuricaemia (high blood uric acid level) is usually observed in gout patients, not all patients with hyperuricaemia have gout.
What are the Symptoms and Signs of a Gout Attack?
A gout attack usually occurs suddenly, resulting in severe pain within a few hours. The joint (most commonly the big toe or knee) becomes extremely painful swollen, warm and red.
Common triggers of gout are:
What Happens if Gout is Not Treated?
First attack will usually settle within a week Patient will remain symptom-free until the next attack.
If gout is not controlled, attacks may become more frequent and last longer. Over time, more joints may be affected and deformed, leading to chronic pain and stiffness.
In some patients with long-standing gout, uric acid crystals get deposited in the tissues. They form lumps (tophi) and are found around the joints or along the outer edge of the ears. Sometimes tophi may rupture and become infected.
Uric acid crystals can also form stones in the kidney and its urine collecting system. These stones can cause pain (colic) and kidney damage
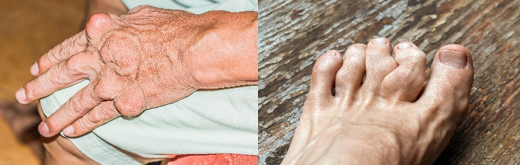
Gout tophi deposits on hands (left) and feet (right).
How is Gout Diagnosed?
A history of sudden joint pain separated by period(s) without pain would strongly suggest gout.
Presence of tophi, uric acid crystals in the fluid removed from an affected joint, or presence of kidney stones can indicate gout.
What is the Treatment for Gout?
Gout can be treated. The treatment aims to treat acute attacks and lower uric acid levels in the long-term to a level that prevents future gout attacks.
What should I do during an acute gout attack?
- Rest your joints.
- Take medication to reduce inflammation. (Please seek your doctor's advice.)
Medications for acute gout attacks
-
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
-
Colchicine (0.5mg) two to three times a day. Common side effects include diarrhoea, nausea and abdominal cramps. It may also be used to prevent attacks of gout.
-
Corticosteroids.
Patients who are unable to take NSAIDs may need oral corticosteroids. Steroids may sometimes be injected into the affected joint to provide relief.
Long-term use of NSAIDS and steroids should be avoided due to their side effects.
-
Urate
Lowering Medications
These effective medications lower your blood uric acid levels and prevent gout attacks. Over time, they reduce tophi sizes and uric acid crystals are prevented from forming in your kidneys.
For most patients with gout, the ideal uric acid level aimed for is below 360μmol/L; for those with severe gout (presence of tophus in particular), it should be below 300μmol/L.
Note that stopping these medications may result in recurrence of gout attacks. They should be taken long-term and continued during a gout attack.
A.
Allopurinol and Febuxostat
These medications prevent the formation of uric acid.
B.
Probenecid and Benzbromarone
These medications increase uric acid excretion in urine. Patients should drink plenty of fluids when taking these medications to prevent stones from forming in the kidneys.
Other Measures to Prevent Attacks
Diet plays an important role in gout management. The general principles are:
- Avoid food and drinks with high fructose corn syrup and limit consumption of naturally sweetened fruit juices.
- Avoid alcohol (beer/spirits), red meat, anchovies, sardines, mackerel, organ meat (e.g. brain, kidney, liver, heart) and shell-fish (e.g. scallops, mussels).
- Drink more water and stay well hydrated.
- Lose weight if you are overweight.
Studies have shown that vegetables high in purines (e.g. asparagus and spinach) DO NOT increase the risk of gout.
Surgery
Surgery does not treat gout. However, it may be performed when tophi are infected or joint movements are affected.