What is Anterior Uveitis (Iritis)?
Anterior uveitis is the inflammation of the anterior most portion of the middle coat (uveal tract) of the eyeball. The most common signs and symptoms are sudden onset of pain, redness, watering, photophobia (difficulty in looking at bright light) etc. It may also be associated with slight decrease of vision at times depending on the severity of the inflammation.
What are the Common Symptoms?
The pupil may get adhered to the front surface of the lens (posterior synechiae). There can be small pus-like material in the lower part behind the cornea in advanced stage, which is termed as hypopyon.
What are the Common Signs?
The eye can also be quiet and white without having any of the above-mentioned symptoms, but have signs of damage due to low-grade inflammation.

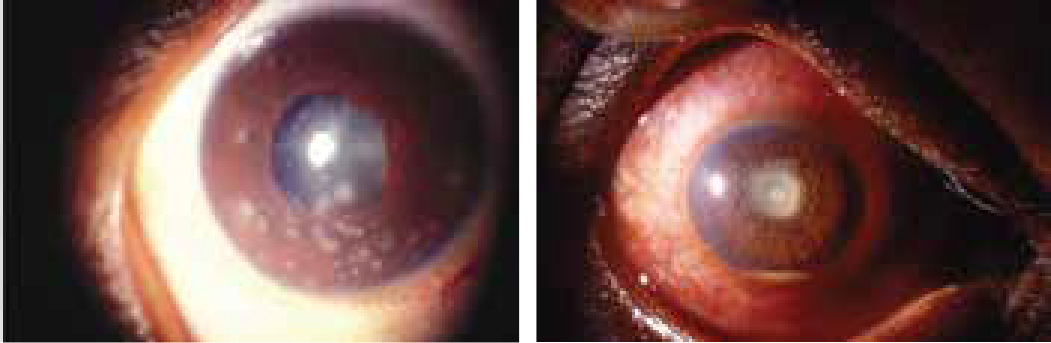
Images showing eyes with anterior uveitis.
Area shaded in red representing the part of the eye which is affected in anterior uveitis.
The disease is predominantly idiopathic, autoimmune or
sometimes infectious in origin.
Autoimmune Causes Include:
- HLA-B27 positive anterior uveitis
- Ankylosing spondylitis
- Reiter's disease
- Sarcoidosis
- Behcet's disease
- Juvenile rheumatoid arthritis
- Ulcerative colitis
- Crohn's disease
- Lens - induced uveitis
- Psoriasis
Infectious Causes Include:
Viral uveitis – Herpes virus, cytomegalovirus,
Bacterial uveitis – Tuberculous uveitis, Syphillitic uveitis
Treatment:
The treatment options include instillation of steroid drops (which are used to suppress inflammation) and cycloplegic or mydriatic eye drops (eye drops that are used to dilate or paralyse the muscles of cilliary body - which help to reduce the pain and prevent the adhesion of pupil with lens).
- The most common steroid eye drop is prednisolone acetate eye drops. The eye drops should be used as per ophthalmologist’s advice only.
- Systemic steroids may be used in severe and unresponsive cases.
- Dark glasses can be worn for intolerance to bright light (photophobia).
- Visual prognosis is usually good if treatment is started early and continued promptly and properly.

What is the Outcome for a Patient with Anterior Uveitis (Iritis)?
The disease is often recurrent and can be unilateral or bilateral. The frequency of recurrence may vary from individual to individual.
Therefore one needs to have a periodic ophthalmic checkup once in 3 to 6 months depending on the severity of the inflammation.