Understanding Knee Replacement
Knee Replacement is a surgical procedure whereby the damaged cartilage is replaced by metallic and plastic parts, called prostheses.
Total Knee Replacement (TKR) is performed when the knee is completely damaged.
Partial Knee Replacement (PKR) can be performed when only isolated compartment(s) of the knee is damaged, usually the medial (inner) compartment.
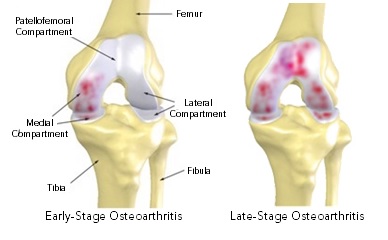
Common Conditions for TKR & PKR
Your doctor may recommend TKR or PKR to you if you have:
Severe pain in the knee that restricts your daily activities
Severe wear and tear of the knee due to conditions such as Osteoarthritis, Rheumatoid Arthritis and Post Traumatic Arthritis
Pain that did not respond well to
non-surgical options, such as weight management, medications and injections
Benefits of TKR & PKR
In most cases, a TKR or PKR surgery will relieve your knee pain and help your knee joint move better. You would be able to resume most of your daily activities such as walking and driving.
Types of Prostheses
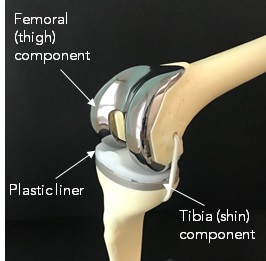
1. Total Knee Replacement Prostheses
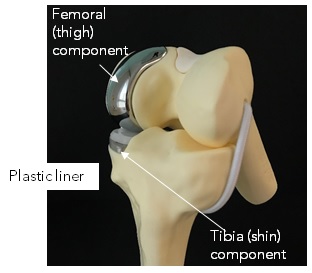
2. Partial Knee Replacement Prostheses
Limitations of TKR & PKR
As the prosthesis is not a perfect replacement for your natural knee, you will have to avoid participating in high-impact activities such as jumping or running that will place excessive stress on the knee.
More Information on Knee Replacement
Before Surgery
You should inform your doctor of any medications you are currently taking, for example aspirin, or any known drug allergies you may have.
There will be a pre-operative education program before the surgery to teach you what to prepare and how to prepare for the surgery
During
Surgery
Before the procedure, the anaesthesia team will administer either general or spinal anaesthesia.
The surgery will last about two to three hours
The metal components are secured to the ends of femur or tibia by bone cement. A plastic liner is attached in between to allow the femoral component to glide smoothly over the tibia and support the body weight.
After
Surgery
You may experience post-operative pain following the knee replacement. Your doctor will give you medications to manage the pain.
You may also experience some stiffness in your operated leg. While at rest, you will be wearing compression pumps to encourage blood flow. You will also wear anti-embolism stockings to help prevent blood clot formation in the deep veins (called Deep Vein Thrombosis, or DVT).
To aid recovery, you will need to undergo rehabilitation with our physiotherapist or nurse who will set specific goals for you to achieve.
Risks Associated with TKR Surgery
While serious post-operation complications are not common in TKR or PKR patients, potential complications that may occur (but not limited to) are:
These risks will be explained to you in detail during your consultation with your doctor. Your doctor will also assess your health condition before the operation.
Length of Hospital Stay
Patients who have undergone TKR procedure without complications usually stay in the hospital for
1 to 3 days.
For PKR procedure, patients usually stay in the hospital for 1 to 2 days. Some patients can even be discharged on the same day, a few hours after the surgery.
Your length of stay is dependent on how well you recover. Participating in physiotherapy sessions can help to speed up your recovery.
Post Total Knee Replacement Exercises
The videos below demonstrates bed exercises that can be done after total knee replacement surgery.