Download PDF, 400KB, PDF
What is Myasthenia Gravis?
Myasthenia gravis (MG) is a condition which causes certain muscles to become tired and weak easily. The muscles controlling the movement of the eyeball and eyelids are commonly affected.
What are the Symptoms?
Patients may experience drooping of one or both eyelids, or double vision which disappears upon closing either eye.
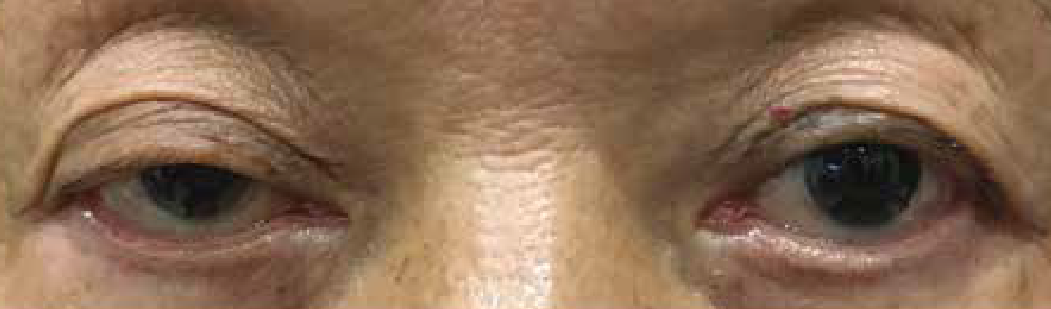
The symptoms are usually worse at the end of the day or when the patients are tired. Rest or sleep usually improves the symptoms temporarily. Patients may also notice a fluctuation in their symptoms.
Sometimes, other muscles in the body can be affected, leading to weakness of the arms and legs. There may also be difficulty breathing and swallowing, or a change in the voice. This is called generalized MG.
What Causes it?
MG is an autoimmune condition. An autoimmune condition occurs when your body's immune system mistakenly attacks healthy tissue. In MG, the autoimmune antibodies (Acetylcholine receptor antibodies, AChRAb) attack the muscles. This interrupts the signals from the nerves to the muscles, leading to weakness of the muscles.
Normal Neuromuscular Junction
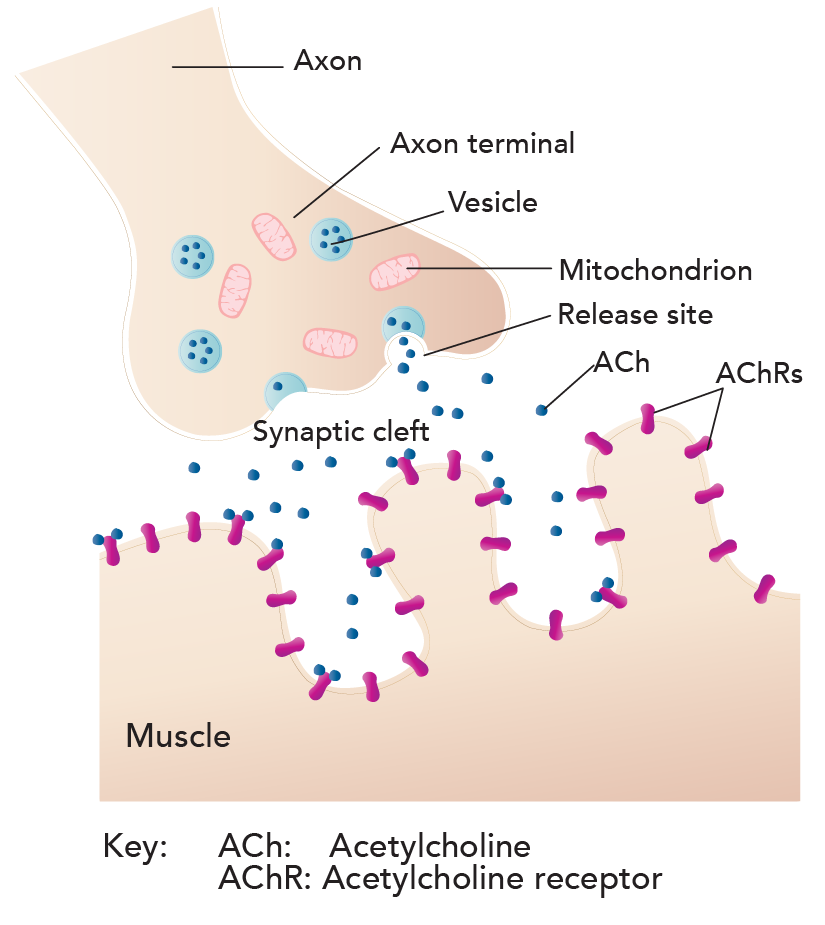
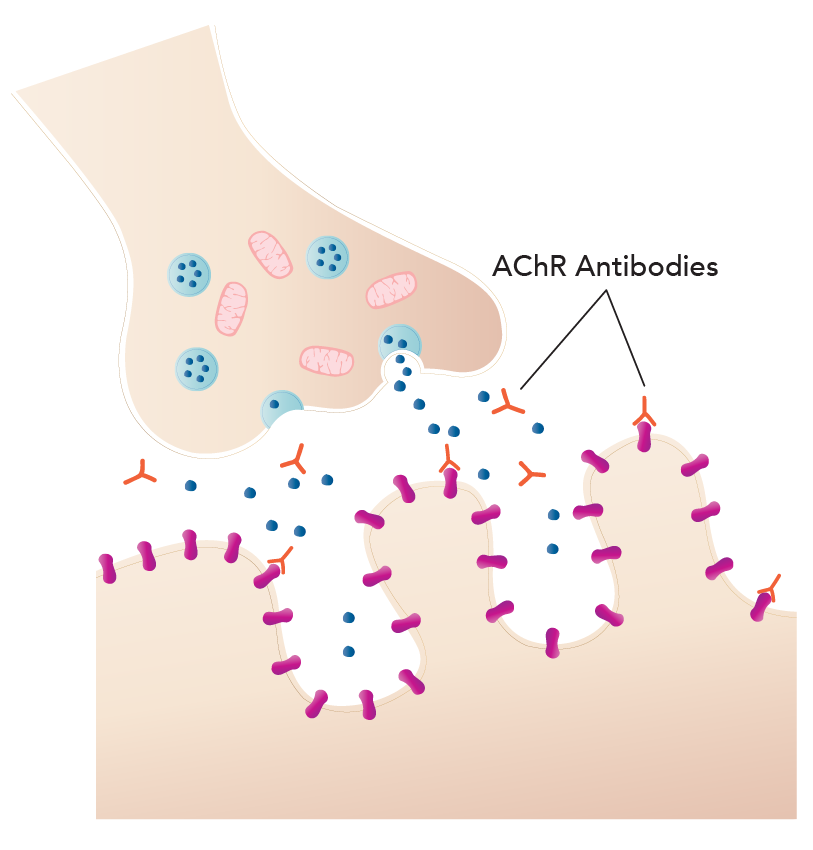
Illustration of a normal neuromuscular junction (above) versus an abnormal one (below) in Myasthenia Gravis.
Myasthenia Gravis
How is it Diagnosed?
The diagnostic process may take a long time as there is no perfect test.
After a thorough history and examination of your condition, your doctor may order investigations which include some or all of the following:
-
Blood tests to check the levels of the autoimmune antibodies (AChRAb): Occasionally, the levels may not be high enough to be detected, and further tests may be required.
-
Ice pack test: Cold packs are placed on your eyelids for a few minutes. Patients with MG may have temporary improvement after application of these cold packs.
-
Electrical testing of the muscles (single fiber electromyography, sfEMG), which involves fine electrodes being placed on or into the muscles to measure the activity. This is done in a specialised neurodiagnostic laboratory.
-
Medication test in the clinic setting (Neostigmine or Tensilon test): A medication is injected into the arm to see if it reverses your symptoms.
-
A treatment trial: You may be started on the medication for MG for a few weeks to see if this improves your symptoms.
-
CT scan
of your chest (thorax): Rarely, a chest tumour called a thymoma can cause MG. Removal of this tumour can sometimes improve your symptoms.
What is the Treatment?
The treatment for MG is primarily medication to counter the effects of the autoimmune antibodies.
These medications include :
1.
Pyridostigmine: This is the most commonly used medication.
- It is not suitable for patients who have electrical problems of the heart; your doctor may perform an ECG beforehand to confirm this.
- Its most bothersome side effect is that of diarrhoea, abdominal and muscle cramps.
- Your doctor will prescribe another medication to be taken as necessary should you suffer from these side effects.
2.
Steroids: Steroids can be very effective, but long-term use may cause some side effects which include:
- High blood sugar
- High blood pressure
- Increased weight
- Osteoporosis
- Bleeding from pre-existing gut or stomach ulcers
- Increased risk of infections
- Abnormalities of the blood salts
- Swelling of the ankles
3.
Steroid-sparing Immunosuppression
- These are tablets which are aimed to replace the steroids you are taking in future, but do not act as quickly.
- These require monitoring in the form of regular blood tests, depending on the type of tablet you are prescribed.
What is the Outlook for this Condition?
You should see your doctor immediately if you experience any of the following :
- Difficulty breathing (especially on lying down)
- Difficulty swallowing
- Change in voice quality
- Weakness of the arms and legs
- Indicating weakness of the neck (weakness when lifting your head)
MG is a long-term condition which will need regular monitoring. However, with medication, most patients are able to continue having a good quality of life.