Download English PDF, 746KB, PDF
What is Hypothyroidism?
Hypothyroidism is a condition when the thyroid gland produces insufficient amounts of thyroid hormone. When this occurs, it can cause a variety of symptoms related to an abnormal slowing of the body’s metabolism rate.
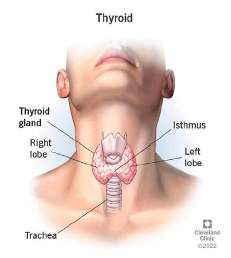
What is the Thyroid Gland?
The thyroid is a butterfly-shaped gland in the front of the neck, located below the larynx (voice box) and above the clavicles (collarbones). It produces thyroid hormone, which regulates how the body uses and stores energy.
Common Causes
- Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis This is the most common cause.
It is an autoimmune disease in which the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks the thyroid gland and damages it.
- Radioactive Iodine Treatment
Hypothyroidism often develops after the use of radioactive iodine treatment for high thyroid hormone production (hyperthyroidism).
- Previous Thyroid Surgery
This is especially if most of the thyroid gland had been removed.
- Medications
These include amiodarone and lithium
- Thyroiditis
The thyroid gland can become inflamed after a viral infection. While this may cause a initial period of hyperthyroidism (high thyroid hormone levels), this may be followed by a period of hypothyroidism.
- Congenital Hypothyroidism
A baby may be born with an insufficient amount of thyroid tissue, or a problem affecting normal thyroid hormone production.
- Problems with the Pituitary Gland
The pituitary gland in the brain is the “master hormone gland” which controls the activity of the thyroid gland. Hence, pituitary disorders can affect thyroid hormone production.
Symptoms
- Cold intolerance (you feel cold more easily compared to other people)
- Weight gain
- Fatigue and weakness
- Constipation
- Depression
- Heavy or prolonged menses
- Slow movements and thoughts
- Hair loss
- Dry, rough skin
Some patients with hypothyroidism may have little or no symptoms, especially if it is mild or has developed very gradually.
These symptoms usually resolve with treatment of hypothyroidism.
Diagnosis
Hypothyroidism can be diagnosed with blood tests that measure the amount of thyroid hormones.
A thyroid function test looks at level of TSH (thyroid-stimulating hormone) and free T4 (thyroxine) in the blood.
T4 is the main thyroid hormone that is produced by the thyroid gland and is expected to be low in hypothyroidism.
TSH is a hormone produced by the pituitary gland. The pituitary gland is the master hormone gland that controls the thyroid gland. This is usually high in hypothyroidism.
Additional investigations such as thyroid antibody tests may be done to help diagnose autoimmune thyroid conditions such as Hashimoto thyroiditis.
Treatment
Hypothyroidism is treated with daily thyroid hormone replacement tablets called levothyroxine. The optimal dose is determined by regular monitoring of thyroid function tests.
Given at the correct dose, levothyroxine is very safe and well-tolerated.
In order not to affect its absorption, levothyroxine should be taken on an empty stomach one hour before calcium and iron-containing supplements, gastric medications and food.